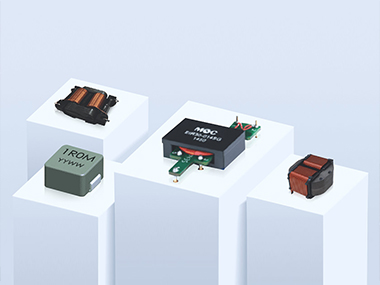
Planar Transformer Technology: Leading the Miniaturization and Efficiency Revolution in Power Systems
A Planar Transformer is an advanced transformer technology that uses PCB (Printed Circuit Board) or multilayer flat winding structures. Compared with traditional wire-wound transformers, planar transformers feature an ultra-low profile, high power density, excellent thermal performance, and consistent manufacturing quality. In recent years, with the rapid growth of power electronics, renewable energy, consumer electronics, and telecommunications, planar transformer technology has gained significant attention and adoption.
Core Advantages

Compact and Lightweight – Thickness can be reduced to just a few millimeters, ideal for portable devices such as USB PD fast chargers.
High Manufacturing Consistency – PCB processes eliminate manual winding errors, ensuring suitability for mass production.
Superior Thermal Performance – Flat structures enable efficient PCB-based heat dissipation, lowering thermal resistance.
Excellent High-Frequency Characteristics – Low leakage inductance (controllable under 1%), ideal for high-frequency switching power supplies.
Technology Development
1. Structural Optimization
Diverse Winding Designs – Multilayer PCB windings use high-precision PCB manufacturing to stack windings, reducing leakage inductance and parasitic capacitance for higher efficiency. Copper foil windings are suited for high-current applications and reduce cost via high-speed stamping processes. Pancake windings with triple-insulated or specialty wires simplify design, shorten development cycles, and lower material costs.
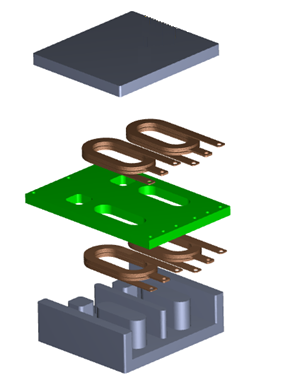
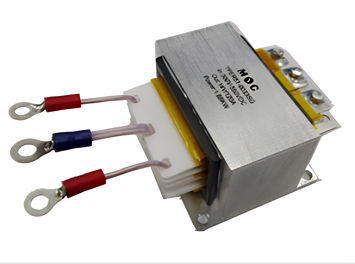
Planar transformer with metal heat sink housing
Magnetic Integration – Integrating transformer and inductor functions into a single magnetic core structure reduces size and increases power density, fitting compact designs.
Enhanced Thermal Management – Metal baseplates improve heat dissipation for high-power planar transformers.
2. Materials Innovation
Magnetic Materials – High-frequency, low-loss magnetic materials reduce size while boosting power density and efficiency, enabling use in MHz-level switching power supplies.
Insulation Materials – High-temperature insulation materials (such as polyimide) ensure high-voltage isolation and long-term reliability.
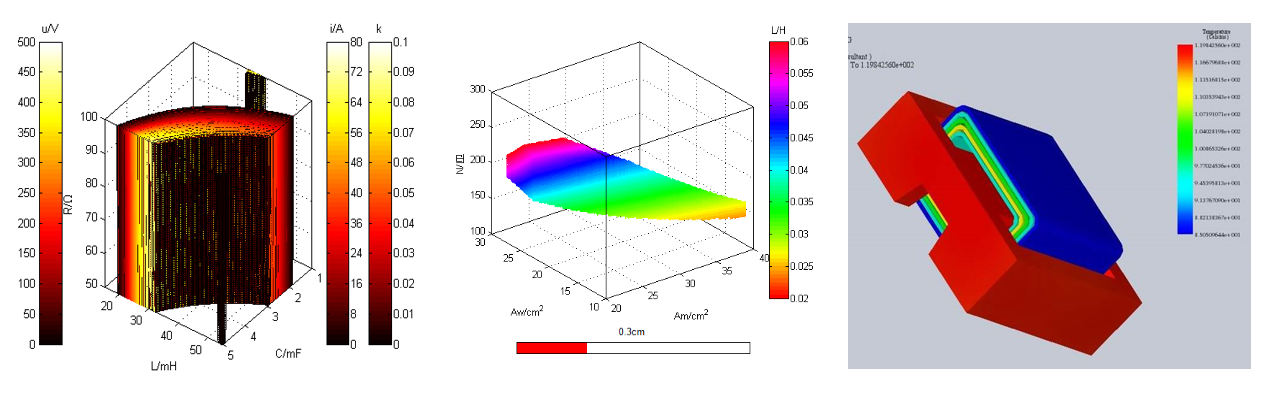
3. AI-Driven Simulation and Design Optimization
Simulation Tools – Software like ANSYS and COMSOL optimizes winding layouts to minimize high-frequency AC resistance (e.g., using Litz wire structures).
Thermal and Magnetic Field Simulation – Design optimization improves thermal dissipation and reduces stress points.
AI Assistance – AI tools accelerate parameter optimization, significantly shortening new product development cycles.
4. Standardization and Modularization
Standardized Coil Designs – Standard series windings can be combined in multiple configurations to meet various performance needs.
Integrated Power Modules – Combining planar transformers with inductors and capacitors creates all-in-one modules (e.g., LLC resonant converters), streamlining the design process.
Application Areas
Thanks to low parasitic parameters, planar transformers excel in high-frequency applications (100 kHz–MHz), particularly for power systems paired with GaN and SiC devices. Key application sectors include:
1. Consumer Electronics
Fast-charging adapters (e.g., GaN chargers) and wireless charging modules.
Power supplies for laptops and LED drivers.


2. Renewable Energy & Automotive Electronics
On-board DC-DC converters for electric vehicles (EV OBCs).
High-frequency isolation converters in micro PV inverters and energy storage systems.
3. Telecommunications & Data Centers
48V bus converters in server power supplies and 5G base station modules.
High-density Power over Ethernet (PoE) devices.
4. Industrial & Medical
Isolated power supplies in PLC systems and high-frequency induction heating equipment.
High-voltage isolation in MRI and X-ray medical devices.
5. Aerospace
Power systems for satellites and UAVs, requiring lightweight, highly reliable solutions.
Future Trends
Higher Frequencies – Advancing to 10 MHz+ with wide bandgap semiconductors (GaN/SiC).
Integration – Combining ICs and passive components for “all-in-one” power solutions.
Intelligent Features – Embedding temperature and current sensors for real-time monitoring.
Green Manufacturing – Lead-free processes and recyclable materials for sustainability.
Conclusion
Through structural innovation and high-frequency design, planar transformer technology is propelling power electronics toward smaller, more efficient, and higher-performance systems. With continued advancements in materials and manufacturing, its adoption in renewable energy, automotive electronics, telecommunications, and other high-demand sectors will keep growing—cementing its role as a cornerstone of next-generation power solutions.
 Mentech Mall
Mentech Mall Group Website
Group Website